School of Design and Environment
The College of Design and Engineering (CDE) came into existence on 1 January 2022 from the merger of the Faculty of Engineering (FoE) and the School of Design and Environment (SDE). Do check cde.nus.edu.sg for the latest on CDE’s programmes.
Undergraduate Education
SDE, together with the Faculty of Engineering (FoE), will adopt a new undergraduate curriculum structure for students enrolled in the new academic year starting in August 2021. Students will read a total of 160 modular credits (or the equivalent of 40 modules), as shown in the following schema:
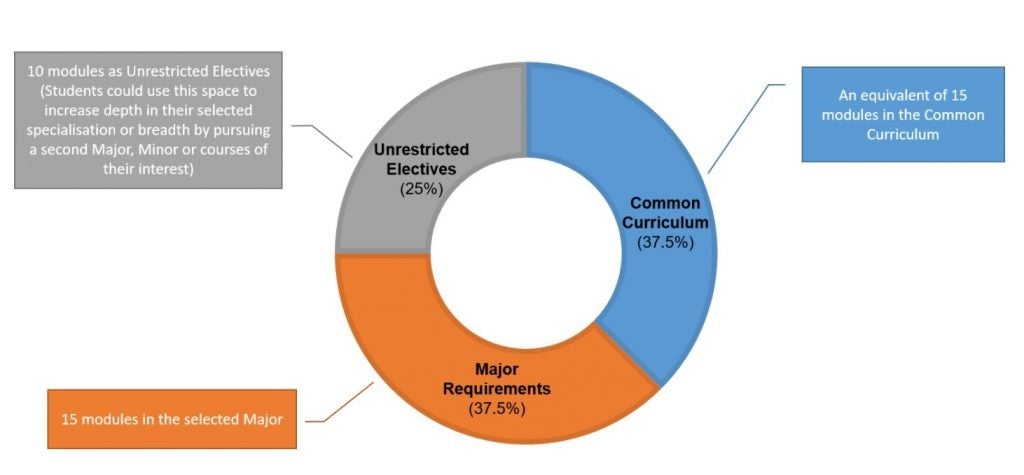
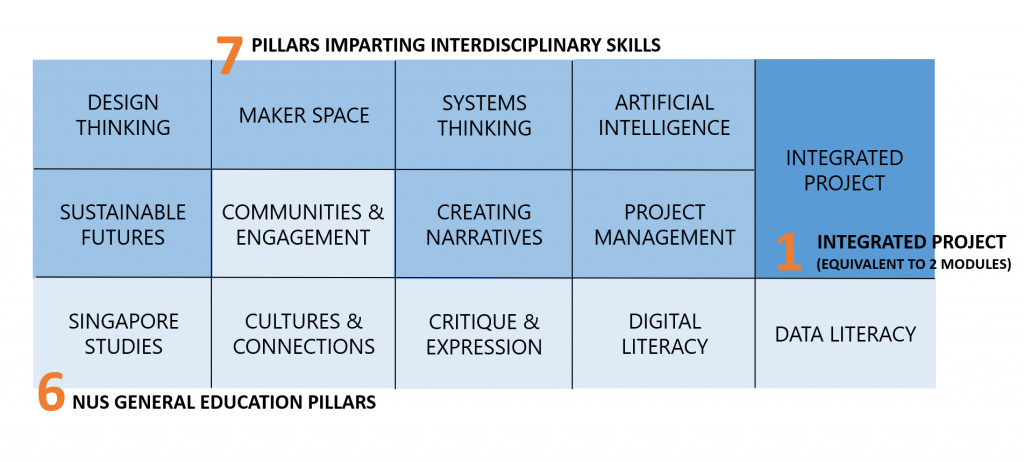
The Common Curriculum is jointly developed by SDE, FoE and 6 industry partners who sit on the task force. It seeks to integrates knowledge and skillsets relevant to the professional training offered by both schools and to equip students with essential 21st century competencies. The following pillars make up the Common Curriculum, comprising 60 MCs (or the equivalent of 15 modules):
For more information, please refer to https://cde.nus.edu.sg/undergraduate.
The BA (Arch) is a four-year honours degree programme that comprises a general programme and three other design-focused tracks – 1) Design, 2) Landscape Architecture (LA) and 3) Urban Planning (UP). The curriculum content for the first three years is common to the general as well as the design-focused tracks.
The general programme terminates at the BA (Arch) degree whereas the design-focused tracks are concurrent with the Master of Architecture (M (Arch)) or Master of Urban Planning (MUP) degree programmes. Only students who have achieved creditable grades in design, i.e. at least a B or B- in design at the third year (depending on the track of study) will be permitted to opt for a design focused tracks.
Students who are not eligible for the design focused tracks will continue in the general programme in their fourth year of study, leading to BA (Arch). Under this programme, students will no longer be required to take the design modules at fourth year. In its place, students will take elective modules with options to focus on Design Computing, Architectural & Urban Heritage or Urban Studies. Students who graduate with a high CAP in the general programme would continue to have the opportunity to pursue other graduate programmes.
Career Opportunities and Professional Registration
Graduates with a BA (Arch) degree who have completed Advanced Architectural Studies on Design Computing, Architectural & Urban Heritage or Urban Studies could work within these areas in architectural practices, government agencies or in research.
Graduates would also have opportunities to work in related fields including and not limited to interior design, industrial design, industrialised building systems, graphic design, commercial art and architectural journalism. Graduates who complete the Landscape Architecture (LA) or Urban Planning (UP) specialisation may also work in fields related to their specialisation.
The BA (Arch) degree does not in itself qualify graduates for registration with the Board of Architects. In order to eventually register as an architect with the Board of Architects, Singapore, BA (Arch) graduates must complete the M (Arch) degree and serve a minimum of two years of practical experience in an architectural practice to be eligible for the Professional Practice Examination conducted by the Board of Architects, Singapore. Those who pass the examination are then eligible to apply for registration as architects in Singapore.
Table 1: Curriculum Structure of the Four-year BA (Arch) Programme
| NO. | MODULES | MCs |
| 1 | University Requirements | 20 |
| a | General Education Modules (GEM) | 20 |
| 2 | Programme Requirements | 108 |
| a | Essential modules taken within the Department | 108 |
| 3 | Unrestricted Electives (UE) 1 | 32 |
| Total | 160 |
1 Requisite modules taken to be considered for admission to the Masters programmes can be used to fulfil the UE requirements
Design-Focused Tracks
Students who have achieved creditable grades (B or B-, depending on the track of study) in design at the third year will be permitted to opt for the design-focused tracks.
The Design track will lead to the M Arch degree programme. The Design track offers students the opportunity to focus on design ideas, innovation and conceptualisation from a theoretical framework.
Students who obtained at least B average in design at third year level are eligible to be considered for Urban Planning track. The UP track allows students to proceed to the Master of Urban Planning programme subjected to fulfilment of the admission requirement.
The Landscape Architecture track enables students to migrate to the Masters in Landscape Architecture (MLA) programme. The LA modules will be offered at the third and fourth year. Students who have opted for the LA track after completion of second year but fail to achieve B- for design modules at third year will pursue the general degree programme.
Listing of Modules
The four-year BA (Arch) programme is structured as follows:
Table 3: BA (Arch) Curriculum – General Programme
| LEVEL 1 | LEVEL 2 | LEVEL 3 | LEVEL 4 | |||||
| Sem 1 | Sem 2 | Sem 1 | Sem 2 | Sem 1 | Sem 2 | Sem 1 | Sem 2 | |
| Design |
AR1101 (8 MCs) |
AR1102 Design 2 (8 MCs) |
AR2101 Design 3 (8 MCs) |
AR2102 Design 4 (8 MCs) |
AR3101 Design 5 (8 MCs) |
AR3102 Design 6 (8 MCs) |
Level 4000 & Above Arch Related Elective (in lieu of Design) (8 MC) |
Level 4000 & Above Arch Related Elective (in lieu of Design) (8 MC) |
| History Theory |
AR2224 Ideas & Approaches in Design (4 MC) |
AR2222 History and Theory of Western Arch (4 MC) |
AR2221 History and Theory of SEA Arch (4 MC) |
|||||
| Urban & Landscape |
AR3223 Introduction to Urbanism (4 MC) |
AR4221 Urban Design Theory and Praxis (4 MC) |
||||||
| Tech Environment |
AR1327 Structural Principles(4 MC) |
AR2524 Spatial Computational Thinking(4 MC) |
||||||
|
AR1328 (4 MC) |
AR2327 Architecture, Structure and Construction(4 MC) |
AR2723 Strategies for Sustainable Arch(4 MC) |
AR3721 Environmental Systems and Construction(4 MC) |
|||||
| General Education Modules (GEM) – 20 MCs Unrestricted Electives (within/outside SDE) (UE) – 32 MCs |
||||||||
Table 4: BA (Arch) Curriculum – Design Track
| LEVEL 1 | LEVEL 2 | LEVEL 3 | LEVEL 4 | ||||||
| Sem 1 | Sem 2 | Sem 1 | Sem 2 | Sem 1 | Sem 2 | Sem 1 | Sem 2 | ||
| Design | AR1101 Design 1(8 MC) |
AR1102 Design 2(8 MC) |
AR2101 Design 3(8 MC) |
AR2102 Design 4(8 MC) |
AR3101 Design 5(8 MC) |
AR3102 Design 6(8 MC) |
AR5801 Options Design Research Studio 1 (8 MC) |
AR5802 Options Design Research Studio 2 (8 MC) |
|
| History Theory |
AR2224 Ideas & Approaches in Design (4 MC) |
AR2222 History and Theory of Western Arch (4 MC) |
AR2221 History and Theory of SEA Arch (4 MC) |
Arch Elective# (4 MC) |
|||||
| Urban & Landscape |
AR3223 Introduction to Urbanism (4 MC) |
AR4221 Urban Design Theory and Praxis(4 MC) |
|||||||
| Tech Environment |
AR1327 Structural Principles (4 MC) |
AR2524 Spatial Computational Thinking (4 MC) |
AR5321 Advanced Architectural Integration # (4 MC) |
||||||
| AR1328 The Tropical Envelope (4 MC) |
AR2327 Architecture, Structure and Construction(4 MC) |
AR2723 Strategies for Sustainable Arch (4 MC) |
AR3721 Environmental Systems and Construction (4 MC) |
Arch Elective# (4 MC) |
|||||
| Management | AR5423 Architectural Practice#(4 MC) |
||||||||
| General Education Modules (GEM) – 20 MCs Unrestricted Electives (within/outside SDE) (UE) – 32 MCs |
|||||||||
#Requisite modules to be considered for admission to the M.Arch programme. These modules can count towards UE requirements
*Additional UEs students have to complete on their own if they are taking the requisite modules listed under # otherwise full 32 MCs of UEs will apply.
Table 6: BA (Arch) Curriculum –Urban Planning Track
| LEVEL 1 | LEVEL 2 | LEVEL 3 | LEVEL 4 | |||||
| Sem 1 | Sem 2 | Sem 1 | Sem 2 | Sem 1 | Sem 2 | Sem 1 | Sem 2 | |
| Design | AR1101 Design 1 (8 MC) |
AR1102 Design 2 (8 MC) |
AR2101 Design 3 (8 MC) |
AR2102 Design 4 (8 MC) |
AR3101 Design 5 (8 MC) |
AR3102 Design 6 (8 MC) |
DEP5101 Urban Analysis Workshop & DEP5101A Qualitative Methods for Urban Planning (8 MCs) |
DEP5103 Urban Planning Studio & DEP5103A Quantitative Methods for Urban Planning (8 MCs) |
| History Theory |
AR2224 Ideas & Approaches in Design (4 MC) |
AR2222 History and Theory of Western Arch (4 MC) |
AR2221 History and Theory of SEA Arch (4 MC) |
|||||
| Urban & Landscape |
DEP5104 Urban & Regional Economics (4 MCs) # |
DEP5102 Urban Planning History &Theory (4 MCs) |
||||||
| UD5521 Planning Process (4 MCs) # |
MUP Elective 2 (4 MCs) # |
|||||||
| AR3223 Introduction to Urbanism (4 MC) |
MUP Elective 1 (4 MCs) # |
MUP Elective 3 (4 MCs) # |
||||||
| Tech Environment |
AR1327 Structural Principles (4 MC) |
AR2524 Spatial Computational Thinking (4 MC) |
||||||
| AR1328 The Tropical Envelope (4 MC) |
AR2327 Architecture, Structure and Construction (4 MC) |
AR2723 Strategies for Sustainable Arch (4 MC) |
AR3721 Environmental Systems and Construction (4 MC) |
|||||
| General Education Modules (GEM) – 20 MCs Unrestricted Electives (within/outside SDE) (UE) – 12 MCs* |
||||||||
#Requisite modules to be considered for admission to the M.UP programme. These modules can count towards UE requirements
*Additional UEs students have to complete on their own if they are taking the requisite modules listed under # otherwise full 32 MCs of UEs will apply.
Teaching Approach
Design modules are taught through design studios. Critique sessions will form part of the studio procedure in teaching. Lecture modules include formal lectures, followed by seminars/tutorials. Field trips, site visits, measurement and study of buildings for research, investigation and documentation may be involved.
Assessment and Examination
Assessment criteria will vary according to subject content. In the Department of Architecture, design modules are assessed by 100% “continuous assessment” (CA). The other essential modules may also be assessed by 100% CA or a combination of CA and Examination.
Students who fail an essential module will retake the module when it is next offered and must sit for the examination in that Semester. A retake module refers to a module where students have to attend lectures and tutorials and complete assignments and examinations. A new CA grade has to be obtained.
Students who fail a GEM/UE module may either replace it with a new GEM/UE module or retake the failed module the following year. There is no limit to the number of times a student may retake the same GEM/UE module.
A student who has passed the examination of a module will not be permitted to retake the same module for the purpose of improving his/her grade. This condition does not apply to the Design modules where the prerequisite for progression to the next level is a ”C” or “S” grade. Students who achieve a ”D” or “U” grade will be required to retake the Design module.
Progression of Students
Please see the table below:
| Minimum MCs (in general) for promotion to the next level | ARK1 -> ARK2 [>=40 MC] ARK2 -> ARK3 [>=80 MC] ARK3 -> ARK4 [>=120 MC] |
| Additional requirements |
Must pass Design with a minimum “C” or “S”** grade ** Applicable to AR1101/ AR1102 if students declare S/U for the module(s) under the S/U policy (for 2016/17 cohort onwards) |
Graduation Requirements for four-year BA (Arch) Programme
Students are required to take all essential modules offered in the semester to which they have progressed, provided they have passed the relevant prerequisites. In addition, they may take modules to satisfy University and other requirements.
Minimum Graduating criteria for
- BA (Arch) Hons: Minimum Grade C for Design and CAP 3.00
- BA (Arch): Minimum Grade C for Design and CAP 2.00
Students who exit the concurrent degree programme at the end of BA (Arch) Year 4 and consequently seek admission to M (Arch), M (LA) or M (UP) would be required to fulfil a minimum CAP of 3.50 and other criteria governing admission as determined at the point of application.
Advanced Placement Credits
Polytechnic diploma holders admitted to the programme may be granted advanced placement credits (APCs) for relevant modules. This is subject to Departmental consideration, given the wide range of subject modules from the polytechnics.
For up-to-date APCs list, please refer to:
https://cde.nus.edu.sg/arch/programmes/bachelor-of-arts-in-architecture/advanced-placement-credits-apcs-for-baarchitecture-programme/
The Bachelor of Arts (Industrial Design) (BA(ID)) programme at NUS was first offered in 1999 with support from the Faculty of Engineering and School of Business.
The BA (ID) programme is a four-year undergraduate honours programme, consisting of courses crafted with our synergistic three-pronged approach:
- Design Thinking: Out-of-box innovation strategies and investigative methods to discover new ideas and unmet needs.
- Multi-Disciplinary Aptitudes: Behavioral sciences, social economics, business strategy, engineering and technology knowledgedevelop entrepreneurial strategic thinking and holistic problem-solving.
- Artistic Sensibility: Training of imagination, taste, and craft-like ability to give pleasing and appropriate aesthetics and emotion to ideas, through traditional and 2D/3D digital means, so that solutions are both functional and desirable.
The combined approaches equip our graduates with high-level strategic thinking, and enable them to translate problems and ideas to tangible, desirable solutions, i.e. meaningful products, environments and experiences that people love to have, love to use – and those which have a big impact on lives.
As part of our strategy to be thought leaders in industry, a major component of the course is a series of industry-sponsored ‘vertical studio platforms’. These are project teams comprising a mix of year 2 to year 4 students, encouraging cross-pollination of thoughts, skills and learning.
In these platforms, students tackle both conceptual and real-life projects led by our industry collaborators, e.g. Asus, Dell, L’Oreal, Estee Lauder, BMW Group DesignworksUSA, Tupperware, Toshiba, Osim, ICI, Swarovski, HansGrohe, Risis and Nakamichi.
Students may customize their individual course during the 4 years by selecting from amongst these different industry platforms – Each student will get the opportunity to be involved in 6-7 of these projects.
The programme has been proven to be effective in grooming students for the design and related industries. Apart from the success in local and international competitions and awards, recent graduates have achieved recognition in gaining scholarships for further studies as well as being placed in well-known design practices and reputable companies.
Students can also opt to do a second major in Management (Technology), offered by School of Business, in four years.
International Exposure
To broaden our students’ exposure to global challenges, two-thirds of each cohort are involved in one-semester overseas exchange programme during their 3rd year. Students typically go to distinguished design schools in Switzerland, France, Japan, Netherlands, Finland, USA, Germany, Italy and China.
Career Opportunities
Students are educated to become expert innovators and master problem-solvers. These attributes make them highly valuable in any industry.
Graduates pursue careers as industrial designers, interaction designers, brand and packaging designers, design managers, product managers and innovation consultants. It is also possible for industrial designers to rise to corporate leadership levels in the areas of creative innovation or design. These are highly-coveted positions, such as Chief Designer, Chief Innovation Officer (CIO), etc.
Armed with design, business and technological knowledge, graduates will be well-positioned to serve in R&D companies, technology start-ups, design consultancies, service industries, marketing sectors and government agencies as well as in design education.
Table 1: Curriculum Structure of the BA (Industrial Design) Programme
| NO. | MODULES | MCS |
| 1 | University Requirements | 20 |
| a | General Education Modules (GEM) | 20 |
| 2 | Programme Requirements | 108 |
| a | Essential modules taken within the Department | 108 |
| 3 | Unrestricted Electives (UE) | 32 |
| Total | 160 |
Table 2: BA (ID) programme is structured as follows for Cohort admitted in AY2018/2019 onwards
| Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Level 4 | ||||||
| 1st Semester | 2nd Semester | 3rd Semester | 4th Semester | 5th Semester | 6th Semester | 7th Semeste | 8th Semester | ||
| General Education 5 Pillars (20MC) |
GEQ1000 Asking Question (4MC) |
GER1000 Quantitative Reasoning (4MC) |
Human Cultures – 4MC Thinking & Expression – 4MC S’pore Studies – 4MC |
||||||
| Industrial Design Major Requirements (108MC) | Design Lecture Modules | ID2323 Technology for Design (4MC) |
|||||||
| ID1113 Modelling and Sketching for Design (4MC) |
ID1322 Materials and Manufacturing for Industrial Design (4MC) |
ID2116 (NEW) Computing for Design (4MC) |
|||||||
| ID1223 History & Theory of Industrial Design (4MC) |
ID1121 Human Centred Design (4MC) |
ID2111 Computer Aided Industrial Design (4MC) |
ID4121 Project Research (4MC) |
||||||
| Design Studio | ID1105 Design Fundamentals 1 (8MC) |
ID1106 Design Fundamentals 2 (8MC) |
ID2105 Design in Context & Sustainability (8MC) |
ID2106 Design Platforms 1 (10MC) |
ID3105 Design Platforms 2 (10MC) |
ID3106 Design Platforms 3 (10MC) |
ID4105 Design Platforms 4 (10MC) |
ID4106 Design Thesis Project (12MC) |
|
| Unrestricted Electives (within/outside SDE) (UE) – 32 MCs | |||||||||
Table 3: Industrial Design Unrestricted Electives
| Optional Industrial Design Electives |
| Semester 1 |
| ID2113 Visual communication Design (4MC) |
| ID3124 Creative Communication & Design Argumentation (4MC) |
| ID3125 Colours, Materials & Finishing (4MC) |
| Semester 2 |
| ID2112 Digital Design & Fabrication (4MC) |
| ID2114 Form, Material, & Making (4MC) |
| ID2115 Digital Sketching & Painting (4MC) |
| ID2122 Ecodesign & Sustainability (4MC) |
Teaching Approach
Design modules are taught through design studios. Critique sessions will form part of the studio procedure in teaching. Lecture modules include formal lectures, followed by seminars/tutorials.
Assessment and Examination
Assessment criteria will vary according to the modules offered. In the Division of Industrial Design, design modules are assessed by 100% “continuous assessment” (CA). The other essential modules may also be assessed by 100% CA or a combination of CA and examination.
Students who fail an essential module will retake the module when it is next offered and must sit for the examination in that Semester. For a retaken module, students have to attend lectures and tutorials and complete assignments and examinations. A new CA grade has to be obtained.
Students who fail a GEM/SS/Breadth/UE module may either replace it with a new GEM/SS/Breadth/UE module or retake the failed module the following year. There is no limit to the number of times a student may retake the same GEM/SS/Breadth/UE module.
A student who has passed the examination of a module will not be permitted to retake the same module for the purpose of improving his/her grade.
Progression of Students
Please see the table below:
| Minimum MCs (in general) for promotion to the next level | IDS1 -> IDS2 [>=40 MC] IDS2 -> IDS3 [>=80 MC] IDS3 -> IDS4[>=120 MC] |
Graduation Requirements for four-year BA (ID) (Hons) Programme
Students are required to take all essential modules offered in the semester to which they have progressed, provided they have passed the relevant prerequisites. In addition, they may take modules to satisfy University and other requirements. ‘Fulfilling’ Modular Credits means reading and passing the modules, which carry the Modular Credits.
Advanced Placement Credits
Polytechnic diploma holders admitted to the programme may be granted advanced placement credits (APCs) for relevant modules. This is subject to Departmental consideration, given the wide range of subject modules from the polytechnics.
For up-to-date APCs list, please refer to this link.
The Bachelor of Landscape Architecture (BLA) is a four-year Honours degree programme that prepares students to respond to multifaceted socio-ecological issues in Asia through critical thinking, analytical inquiry, and creative expression. BLA provides core foundation training in skills and knowledge that equips our graduates for professional practice or entry into advanced Master degree programmes. Relevant topics, including tropicality, site specificity, boundaries and scales, densification, multifunctionality, and placemaking are played out in the programme through integrated learning platforms in design studios and lectures. BLA is taught in unique education settings that concurrently promotes speculation in design and at the same time being produces grounded and action-oriented design outcomes relevant to real life issues.
For more information, please refer to:
https://www.cde.nus.edu.sg/arch/programmes/bachelor-of-landscape-architecture/
The four-year direct honours Bachelor of Science (Project & Facilities Management) (BSc (PFM)) programme combines management and technologically oriented subjects in a holistic and integrated manner. It is designed to develop leaders for the built environment sector.
Core areas of study
- Project Management
- Contract Management / Quantity Surveying
- Facilities Management
- Event Management
Eligible BSc (PFM) undergraduates may opt for a second major in Management (offered by NUS Business School) or in Management (Technology) (jointly offered by NUS Business School and Faculty of Engineering). Students may also opt for a Double Degree Programme.
Polytechnic diploma holders who are granted Advanced Placement Credits (APCs) may complete the programme in 3.5 years.
Table 1: Curriculum Structure of the BSc (Project and Facilities Management) (Hons) Programme for students admitted from AY2019/2020 onwards
| No. | Modules | MCs |
| 1 | UNIVERSITY REQUIREMENTS | 20 |
| 1.1 | General Education Modules(GEM)^ Students will be required to read one GEM from each of the following five pillars |
|
| a | Human Cultures (GEH) | 4 |
| b | Asking Questions (GEQ) | 4 |
| c | Quantitative Reasoning (GER) | 4 |
| d | Singapore Studies (GES) | 4 |
| e | Thinking and Expression (GET) | 4 |
| 2 | PROGRAMME REQUIREMENTS | 108 |
| a | Essential modules | 56 |
| b | Project and Event Management (PEM) modules | 8 |
| c | Contract and Cost Management (CCM) modules | 12 |
| d | Facilities and Infrastructure Asset Management (FIAM) modules | 12 |
| e | Integrated Digital Delivery Management (IDDM) modules | 12 |
| f | Dissertation (for students on Dissertation track)* OR Any 2 Programme Electives (for students on Non-Dissertation track)** |
8 |
| 3 | UNRESTRICTED ELECTIVES (UE) | 32 |
| Total | 160 |
Note:
^Please refer to GEM website (http://www.nus.edu.sg/registrar/general-education.html) for more details on the GEM requirements.*Dissertation track (students with CAP 3.50 and above):
– 25modules (100MCs) + 1 Dissertation (8 MCs) = 26modules (108MCs)
– Minimum 20 MCs of Level 4000 modules = PF4102 (4 MCs) + PF4101 (8 MCs) + 2 other Level 4000 Programme Electives/ non-PFM modules (8 MCs)
**Non-dissertation track (students with CAP below 3.50):
– 25modules (100MCs) + 2 programme electives (8MCs) = 27modules (108MCs)
– Minimum 20 MCs of Level 4000 modules = PF4102 (4 MCs) + 4 other Level 4000 Programme Electives/ non-PFM modules (16 MCs)
Table 2: BSc (Project and Facilities Management) Programme Structure for students admitted from AY2019/2020 onwards
| Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Level 4 | |||||
| Essential | Sem 1 | Sem 2 | Sem 3 | Sem 4 | Sem 5 | Sem 6 | Sem 7 | Sem 8 |
| PF1101 Fundamentals of Project Management (4 MCs) |
PF2109 Project Feasibility (4 MCs) |
PF2108 Project Cost Management (4 MCs) |
PF3104 Project Execution (4 MCs) |
PF4102 Contract and Procurement Management (4 MCs) |
||||
| PF1106 Introduction to Measurement (4 MCs) |
PF1103 Digital Construction (4 MCs) |
PF2107 Construction Technology (4 MCs) |
PF2103 Measurement (Building Works) (4 MCs) |
|||||
| PF1107 Project and Facilities Management Law (4 MCs) |
PF1108 Introduction to Building Performance (4 MCs) |
PF2102 Structural Systems (4 MCs) |
PF2110 Fundamentals of Facilities Management (4 MCs) |
PF3105 Research Methods (4 MCs) |
PF4101 Dissertation (optional for CAP below 3.50) (8 MCs) |
|||
| Project & Event Mgt (PEM) | PF2203 Quality and Productivity Management (4 MCs) |
PF3208 Project Leadership (4 MCs) |
PF4209 Construction Enterprise Management (4 MCs) |
PF4208 Safety and Health Management (4 MCs) |
||||
| PF2305 Event Management (4 MCs) |
PF2306 Event Management Case studies (4 MCs) |
|||||||
| Contract & Cost Mgt (CCM) | PF2205 Project Finance (4 MCs) |
PF3205 Advanced Measurement (4 MCs) |
PF3201 Measurement (Specialist Works) (4 MCs) |
PF4203 Project Dispute Management (4 MCs) |
||||
| PF3207 Project Management Law (4 MCs) |
||||||||
| Facilities & Infrastructure Asset Mgt (FIAM) | PF3307 Strategic Facilities Management (4 MCs) |
PF3305 Facilities Planning and Design (4 MCs) |
PF4306 REITs Facilities Management (4 MCs) |
|||||
| PF2505 M&E Systems (4 MCs) |
PF3301 Maintainability of Facilities (4 MCs) |
PF3306 Facilities Management Law and Contracts (4 MCs) |
PF4309 Infrastructure Operations and Maintenance (4 MCs) |
|||||
| PF3504 Energy Management (4 MCs) |
||||||||
| Integrated Digital Delivery Mgt (IDDM) | CS1010S Programming Methodology (4 MCs) |
PF2502 Development Technology and Management (4 MCs) |
PF3209 Building Information Modelling(4 MCs) |
PF3502 Smart Facilities (4 MCs) |
PF4501 Total Building Performance (4 MCs) |
|||
| PF2504 Materials Technology (4 MCs) |
PF4211 Additive Manufacturing for Construction (4 MCs) |
PF4502 Green Development (4 MCs) |
||||||
| PF4210 Project Studio (4 MCs) |
||||||||
| Internship (UE) | F2402 Work Experience Internship/ PF3401 Practical Training Scheme (4 MCs) |
PF2402 Work Experience Internship/ PF3401 Practical Training Scheme (4 MCs) |
||||||
The Qualifying English Test (QET) is an English Language test set by the Centre for English Language Communication. It must be taken by students who do not possess the necessary English Language qualifications when they enter the university. More information can be found at: http://www.nus.edu.sg/celc/programmes/qet.html
Length of Degree Programme
The programme is designed to allow students to progress at their own pace. Students who are able to progress at a faster pace can complete the programme in three-and-a-half years if they take additional essential modules in semester two of their Second and Third Levels. Those doing the programme at a regular pace should complete it in four years.
Assessment and Examination
Students are assessed on a mixture of class work and end-of-semester examinations for each module they had registered for in the semester. Continuous Assessment (CA) may be in the form of essays, laboratory work, projects, reports, or tests. Students’ performance during tutorials may be assessed as part of the CA.
Students who fail in an essential module have to retake the essential module the following year. For a retaken module, students have to attend lectures and tutorials and complete assignments and examinations. A new CA grade has to be obtained.
Students who fail a non-essential module may either replace it with a new module or retake the failed module the following year. There is no limit to the number of times a student may retake the same non-essential module.
Students who have passed any module are not allowed to retake the module to improve their grades.
Progression of Students
Please see the table below:
| Minimum MCs (in general) for promotion to the next level | PFM1 -> PFM2 [>=40 MC] PFM2 -> PFM3 [>=80 MC] PFM3 -> PFM4 [>=120 MC] |
Requirements for four-year BSc (Project and Facilities Mgt) (Hons) Programme
Students have to take all essential modules offered in the semester to which they have progressed, provided they have passed the relevant prerequisites. In addition, they may take modules to satisfy University and other requirements. To graduate, a student must obtain a minimum of 160 MCs in accordance with the requirements shown in Table 1. ‘Fulfilling’ Modular Credits means reading and passing the modules which carry the Modular Credits.
Advanced Placement Credits
Polytechnic diploma holders admitted to the programme may be granted advanced placement credits (APCs) for relevant modules. This is subject to Departmental consideration, given the wide range of subject modules from the polytechnics.
For up-to-date APCs list, please refer to this link.
The Department of Real Estate offers a full-time BSc (Real Estate) undergraduate programme. This is a professional honours degree programme to be completed in four years by students proceeding at a normal pace. The programme is fully recognised by renowned local and foreign professional institutions.
Student may opt to complete a specialisation in real estate finance by completing 24 MCs of distinctive programme elective modules.
Career Opportunities
Students in this programme should be interested in the built environment covering issues from planning, development, management, and the social, economic, political to technical facets of the built environment. In Singapore, career opportunities for Real Estate graduates are found in both public and private sectors. Graduates are employed in the fields of real estate fund management (including REITs), real estate development and investment, urban planning, property valuation and corporate real estate management.
Table 1: Curriculum Structure of the BSc (Real Estate) (Hons) Programme
| NO. | MODULES | MCS |
| 1 | University Requirements | 20 |
| a | General Education Modules (GEM) | 20 |
| 2 | Programme Requirements | 108 |
| a | Essential modules taught by the Department of Real Estate | 76 |
| b | Essential modules taught by other Departments | 4 |
| c | FYP Dissertation OR FYP Academic Exercise plus programme elective |
8 |
| d | Programme elective modules | 20 |
| 3 | Unrestricted Electives (UE) | 32 |
| Total | 160 |
Programme Structure
The programme is structured into three core areas of study as listed below:
Core Areas
- FINANCE • INVESTMENT • ANALYTICS •
Real Estate Investment and Asset Management
Real Estate Finance and Securitisation
Real Estate Portfolio and Risk Management
International Real Estate
- DEVELOPMENT • ENTERPRISE • SERVICES
Land and Business Law
Real Estate Valuation
Real Estate Business and Property Development
Real Estate Consultancy
Real Estate Marketing and Facilities Management
- ECONOMICS • PLANNING • POLICY
Planning Theories and Techniques
Public Policy and Real Estate Markets
Sustainable Development
Town Planning
Data Analytics
Urban Economics
Table 2A: BSc (Real Estate) Programme Structure (Normal Track)
| Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Level 4 | ||||
| Semester 1 | Semester 2 | Semester 1 | Semester 2 | Semester 1 | Semester 2 | Semester 1 | Semester 2 |
| RE1701 Urban Land Use and Development |
RE1704 Principles of Real Estate Economics |
ES2007D Professional Communication |
RE2704 Introduction to Real Estate Valuation |
RE3701 Real Estate Investment Analysis |
RE3703 Advanced Real Estate Economics (Pre‐req: RE2705) |
RE4711 FYP Dissertation (8MC) OR RE4712 FYP Academic Exercise (4 MC) + 1 PE |
|
| RE1702 Real Estate Data Analytics |
RE1705 Real Estate Finance and Accounting |
RE2701 Urban Planning (Pre‐req: RE1701) |
RE2705 Urban Economics |
RE3702 Property Tax and Statutory Valuation (Pre‐req: RE2704) |
RE3704 Real Estate Marketing |
RE4701 Real Estate Development (Pre‐req: RE3703, RE3704) |
PE4 |
| RE1703 Principles of Law for Real Estate |
RE1706 Design and Construction |
RE2702 Land Law (Pre‐req: RE1703) |
RE2706 Real Estate Finance |
PE1 | PE2 | RE4702 Professional Practice and Ethics (Pre‐req: RE1703) |
PE5 |
| GE | GER1000 | RE2708 Computational Thinking and Programming for Real Estate |
RE2707 Asset and Property Management (Pre‐req: RE1706) |
UE2 | UE4 | PE3 | UE7 |
| GE | GE | GE | UE1 | UE3 | UE5 | UE6 | UE8 |
Students who have not passed the Qualifying English Test at the time of admission to the University must take an additional module in English in Level One. Students who are exempted from the Qualifying English Test need not do an additional module in English.
TABLE 2B: BSC (REAL ESTATE) PROGRAMME STRUCTURE (Fast TRACK)
| Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Level 4 | ||||
| Semester 1 | Semester 2 | Semester 1 | Semester 2 | Semester 1 | Semester 2 | Semester 1 | Semester 2 |
| RE1701 Urban Land Use and Development |
RE1704 Principles of Real Estate Economics |
ES2007D Professional Communication |
RE2704 Introduction to Real Estate Valuation |
RE3701 Real Estate Investment Analysis |
RE4711 FYP Dissertation (8MC) OR RE4712 FYP Academic Exercise (4 MC) + 1 PE |
||
| RE1702 Real Estate Data Analytics |
RE1706 Design and Construction |
RE2701 Urban Planning (Pre‐req: RE1701) |
RE2706 Real Estate Finance |
RE3702 Property Tax and Statutory Valuation (Pre‐req: RE2704) |
PE1 | RE4701 Real Estate Development (Pre‐req: RE3703, RE3704) |
|
| RE1703 Principles of Law for Real Estate |
GEQ1000 | RE2702 Land Law (Pre‐req: RE1703) |
RE2707 Asset and Property Management (Pre‐req: RE1706) |
RE3703 Advanced Real Estate Economics (Pre‐req: RE2705) |
PE2 | RE4702 Professional Practice and Ethics (Pre‐req: RE1703) |
|
| RE1705 Real Estate Finance and Accounting |
GE | RE2705 Urban Economics |
GE | RE3704 Real Estate Marketing |
PE3 | PE4 | |
| GER1000 | GE | RE2708 Computational Thinking and Programming for Real Estate |
UE6 | UE7 | UE8 | PE5 | |
Polytechnic diploma holders may be granted advanced placement credits (APC) up to 20 MCs for Unrestricted Elective modules.
Students who have not passed the Qualifying English Test at the time of admission to the University must take an additional module in English in Level One. Students who are exempted from the Qualifying English Test need not do an additional module in English.
Students admitted can undertake one of the 2 academic routes:
- BSc (Real Estate)
- BSc (Real Estate) with Specialisation in Real Estate Finance
A specialisation will be awarded if a student completes a basket of 24 MCs (6 modules) of stipulated Programme Electives. The specialisation will be noted in a student’s transcript. It is not compulsory for students to pursue a specialisation.
A student may opt to complete a specialisation in real estate finance after they have completed the fourth semester.
Table 3: Real Estate Finance Specialisation Programme Electives
| Module Code | Real Estate Finance Specialisation (REFS) Programme Electives | Pre-Requisites |
| RE3802 | Real Estate Finance Law | RE1703 |
| RE3805 | Corporate Investment in Real Estate | RE3701 |
| RE3807 | Corporate Finance for Real Estate | RE3701 |
| RE4711 | FYP Dissertation (8MC)* | Nil |
| RE4712 | FYP Academic Exercise (4MC)* | Nil |
| RE4801 | Real Estate Internship Programme* | Nil |
| RE4803 | REIT Management | RE3701 |
| RE4804 | Real Estate Securitisation | RE3701 |
| RE4806 | Real Estate Finance Seminar | RE3701 |
| RE4807 | Real Estate Risk Analysis and Management | RE3701 |
*For RE4711 FYP Dissertation, RE4712 FYP Academic Exercise and RE4801 Real Estate Internship Programme to be counted as fulfillment towards the REFS, it must be Finance Related and approved by the Department. If RE4711 is accepted, student must still complete another 5 modules from the REFS programme electives.
Students who are not completing the real estate Specialisation are required to complete 20 MCs of programme electives in any combination (except RE4806 Real Estate Finance Seminar). In addition to the 20 MCs, students are still required to complete either RE4711 FYP Dissertation or RE4712 FYP Academic Exercise.
Table 4: Other Programme Electives
| Module Code | Other Programme Electives | Pre-Requisites |
| RE2801 | Research Methodology in Real Estate | RE1702 |
| RE3803 | Strategic Asset Management | RE2702 |
| RE3804 | Real Estate Development Law | RE2702 |
| RE3806 | Advanced Real Estate Valuation | RE3702 |
| RE3901 | Advanced Urban Planning | RE2701 |
| RE4802 | Topics in Real Estate (Summer Programme) | Year 2 Modules |
| RE4805 | International Real Estate Development and Investment | RE4701 |
| RE4808 | Urban Challenges and Policies | RE2701, RE3703 |
Table 5: Real Estate Unrestricted Electives
| Module Code | Real Estate Unrestricted Electives | Pre-Requisites |
| RE1901 | Real Estate Wealth Management | Nil |
| RE3000 | Work Experience Internship | Completed at least 4 Semesters and have not accumulated 12 MCs of Internship credits |
| RE3902 | Housing Markets and Policies | Nil |
| RE3903 | GIS for Real Estate | Nil |
Concurrent Degree Programme: BSc (Real Estate) + Master of Urban Planning
BSc (RE) students who are interested in Urban Planning (UP) can also choose to pursue the M (UP) concurrently. After a 5-year candidature, they will get 2 degrees:
- BSc (RE) with a specialisation in UP
- M (UP)
Eligibility Criteria
At the end of the third year in the BSc (Real Estate) course, applicants must obtain a CAP of at least 3.50. Applicants will be subjected to an interview for discretionary admission.
Continuation Criteria at the end of the fourth year
At the end of the fourth year, the candidate of the CDP must have completed RE4711 FYP Dissertation, and also obtain a minimum CAP of 3.00 (for MUP modules only).
Graduating criteria at the end of the 5th year, include a minimum CAP of 3.00 (for MUP modules taken in Year 4 and Year 5).
Student Workload
In any one semester, students are not allowed to take more than 8 modules (excluding English), whether essentials, electives, or GE modules.
Length of Degree Programme
The programme is designed to allow students to progress at their own pace. Students doing the programme at a regular pace should complete it in four years. Students who are able to progress at a faster pace can complete the programme in three-and- a-half years if they take additional modules in each of the four semesters in their Second and Third Levels.
Assessment and Examination
Students are assessed based on a mixture of class work and end-of-semester examinations for each module they had registered for in the semester. Continuous Assessment (CA) may be in the form of essays, projects, reports, or tests. Students’ performance during tutorials may be assessed as part of the CA.
Students who fail in an essential module will have to retake the module the following year. In such instances, students have to attend lectures and tutorials and complete assignments and examinations. A new CA grade has to be obtained.
Students who fail a non-essential module may either replace it with a new module or retake the failed module the following year. There is no limit to the number of times a student may retake the same non-essential module.
Students who have passed any module are not allowed to retake the module to improve their grades.
Progression of Students
Please see the table below:
| Minimum MCs (in general) for promotion to the next level | RST1 -> RST2 [>=40 MC] RST2 -> RST3 [>=80 MC] RST3 -> RST4 [>=120 MC] |
Graduation Requirements for four-year BSc (Real Estate) (Hons) Programme
Students have to take all essential modules offered in the semester to which they have progressed, provided they have passed the relevant prerequisites. In addition, they may take modules to satisfy University and other requirements. To graduate, a student must obtain a minimum of 160 MCs.
Advanced Placement Credits
Polytechnic diploma holders admitted to the programme may be granted advanced placement credits (APCs) for relevant modules. This is subject to Departmental consideration, given the wide range of subject modules from the polytechnics.
For up-to-date APCs list, please refer to this link.
The credit-bearing internship programmes offered by the Departments within SDE are listed below.
For a list of other internship opportunities, please visit Centre for Future-ready Graduates (CFG)’s internship page.
Architecture Internship Programme – Department of Architecture
The internship programme aims to provide opportunities for third year undergraduates to work in architectural or allied firms or organisations with design centric focus to gain the exposure and experience and apply the knowledge learnt in school in the professional setting.
Students are required to perform a structured and supervised internship in a company/organization for 24 weeks during the regular Semester. Weekly logbook as well as internship reports will be used a part of the evaluation of their internship experience.
Practical Training Scheme – Department of the Built Environment
BSc (Project and Facilities Management) students may undertake a twelve-week-long Practical Training Scheme which is normally held at the end of the second semester in the Third Level. The aim of this scheme is to give students essential real-life work exposure in Singapore or abroad. The Department finds suitable placements with an organisation in the construction or real estate industry for students, and their work is supervised by a staff member of the Department, and a senior person within the organisation to which they are attached.
The module will contribute 4 MCs and a CS/CU grade is awarded.
Work Experience Internship – All Departments
Undergraduate students may undertake an approved internship of at least 10 weeks in duration during the vacation period. This module is opened to full-time undergraduate students who have completed at least 60 MCs.* The module recognises that work experiences in fields that may or may not be directly related to the student’s major can lead to viable career pathways.
The module will contribute 4 MCs and a CS/CU grade is awarded.
*Departments may impose additional requirements or pre-requisites.
The School of Design and Environment’s donated scholarships and bursaries are designed to offer generous financial support to our undergraduates. To be considered for the School-Level financial assistance/scholarships and selected NUS-level donated scholarships, please apply through the Office of Financial Aid (OFA) at the Undergraduate Financial Aid portal from February to April every academic year.
School-Level and Department-Level Financial Assistance/Scholarships
Please visit https://cde.nus.edu.sg/undergraduate/apply-to-cde/donated-scholarships-and-bursaries/
More university-wide Scholarships and Financial Aid, visit the following links:
- Scholarships: http://www.nus.edu.sg/oam/scholarships
- Financial aid: http://www.nus.edu.sg/oam/financial-aid
Medals and book prizes are awarded only once in the academic year, after the Semester 2 Examination. In all instances, a prize-winner must be of sufficient merit. He/She must have passed all modules attempted and must be a good overall student. No award will be made unless there is a candidate of sufficient merit.
In general, to be eligible for consideration for an Academic Year Award, a student must have completed a minimum workload of 40 MCs, 80 MCs and 120 MCs for the Year 1, Year 2 and Year 3 awards respectively. In addition, students must have completed at least 36 MCs of graded modules within the academic year of the award.
The exception to this ruling would be students who are involved in internships, accelerated programmes or double degree programmes. For these students, they need to have a minimum of 24 MCs graded modules. In addition, students must have also completed a minimum of 16 MCs in the subject within the academic year.
For a full list of the medals and prizes for SDE undergraduates, please visit https://cde.nus.edu.sg/undergraduate/academic-awards-and-prizes/

