Beat Diabetes Step By Step
Date: Wednesday, March 03, 2021Learn more about diabetes and ways to fight this chronic condition.

1 in 3 Singapore Residents are at a lifetime risk of developing Type 2 diabetes. Just 2 minutes of your time could potentially save your life.
Take the Diabetes Risk Assessment (DRA) to find out if you are at risk now!
Take the DRA
[TAB-WRAPPER] [TAB TITLE="Be Aware" COLOR="#e94f00"]
What is Diabetes?
Diabetes is a long-term medical condition in which the blood glucose levels of a person remain higher than normal all the time. It occurs when the pancreas does not produce enough insulin or when insulin does not work properly. Insulin is a hormone that reduces the blood glucose levels.
There are different types of diabetes:
Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is usually found in people aged 40 and above who are overweight and physically inactive. In some people, the condition is mild and they are able to control their blood glucose with just diet and exercise. However, if the condition gets worse, they may require oral medication or insulin injections in addition to making lifestyle changes. For those who are overweight or obese, losing weight can be significantly beneficial, even if it is a small amount.
Type 1 Diabetes
Usually diagnosed in children or young adults although it can occur at any age, type 1 diabetes results when the pancreas no longer produces insulin. Hence, persons with type 1 diabetes need insulin injections daily.
Gestational Diabetes
Due to the hormonal changes in pregnancy, some women may show high blood glucose levels during pregnancy. These women require specialised obstetric care to prevent complications to the unborn child. In gestational diabetes, the blood glucose levels often return to normal after delivery. However, these women may be at an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
Pre-Diabetes
Pre-diabetes is when your blood sugar level is higher than normal but not high enough yet to be diagnosed as Type 2 diabetes. Studies show that if pre-diabetic persons lose weight and maintain a healthy Body Mass Index (BMI), adopt a healthy diet and engage in regular physical activity, they can reduce their risk of developing type 2 diabetes
[ACCORDION-WRAPPER] [ACCORDION Header="Risk Factors"]
Diabetes can affect anyone. Knowing your risk of diabetes will help identify the changes you need to make to your lifestyle.
You are at an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes if you:
 Have a parent or sibling with diabetes
Have a parent or sibling with diabetes
 Have a BMI of 23.0kg/m2 or higher
Have a BMI of 23.0kg/m2 or higher
 Lead an inactive (sedentary) lifestyle
Lead an inactive (sedentary) lifestyle
 Have high blood pressure
Have high blood pressure
 Have abnormal blood cholesterol/lipid levels
Have abnormal blood cholesterol/lipid levels
 Have a history of gestational diabetes
Have a history of gestational diabetes
 Are 40 years old and above
Are 40 years old and above
 Have impaired glucose tolerance or impaired fasting glucose
Have impaired glucose tolerance or impaired fasting glucose
Leading a healthy lifestyle improves overall health and reduces the risk of developing diabetes. Age and family history increase one's risk of diabetes. So do being overweight or obese, having an unhealthy diet, and not having enough exercise. Uncontrolled diabetes can lead to serious complications. However, the risk of diabetes can be reduced by leading an active and healthier lifestyle.
For people living with diabetes, a healthy lifestyle can complement other treatment options such as insulin and oral medication to better manage the condition. Take small but significant steps to adopt a healthier lifestyle today to see the positive impact they can have on your health later. As you get used to these small changes, they become a part of your daily routine and taking control of diabetes can only get easier.
[/ACCORDION] [ACCORDION Header="Screening"]Diabetes is a ‘silent’ disease in its early stages, and you can feel perfectly well until complications occur. However, a late diagnosis can result in serious and irreversible complications that could have been otherwise prevented through screening. It is therefore important to get yourself screened even if you feel perfectly healthy and experience no symptoms, for regular health screening is the best way to detect diabetes early and obtain timely treatment.
GOING FOR SCREENING

Screening for chronic diseases, including diabetes, is recommended under HPB's
Screen for Life programme for those 40 years old and above. It is conducted
through a fasting blood glucose test, done once every three years.
Under HPB's Screen for Life programme offered by most
CHAS GP clinics,
chronic disease screening (including the doctor consult charges) is available
at the following subsidised rates :
Pioneer Generation
If you are a Pioneer Generation cardholder, the screening test and the first post screening consultation (if assessed that a consultation is required) will be $0.
Health Assist (CHAS) Card Holders
If you are a CHAS cardholder (blue or orange card), you will only need to pay $2 for the screening test and the first post screening consultation (if assessed that a consultation is required). Applicable for both males and females aged 40 and above.
Other Eligible Singaporeans
You will only need to pay $5 for the screening test and the first post screening consultation (if assessed that a consultation is required). Applicable for both males and females aged 40 and above.
Permanent Residents
You will only need to pay $10 (excluding GST) for the screening test. The prevailing doctor consultation rates will be charged accordingly by the respective CHAS GP clinics.
*These rates are only applicable at CHAS GP clinics for the screening tests that are covered under the enhanced Screen for Life subsidies.
CLINICS
Health screening is available at many private medical clinics and polyclinics. Visit our directory for the list of screening locations, or click here to locate your nearest CHAS GP clinic offering SFL screening services.
Learn more about the screening tests and subsidies you are eligible for at screenforlife.sg.
[/ACCORDION] [ACCORDION Header="Test and Diagnosis"]You can test for diabetes by going for a blood glucose test. There are two types of blood glucose tests:
Fasting blood glucose test

A fasting blood glucose test – usually done in the morning – requires you to fast overnight for at least 8 hours prior to the test.
Oral glucose test

An oral glucose tolerance test requires you to fast for at least 8 hours prior to the blood test. During the test you are given a sugary drink. Your blood glucose level will be measured before and at intervals (1 hour and then 2 hours) after the sugary drink is taken. Test results that are positive are repeated with the same testing process on a different day to confirm diagnosis.
Health Screening is heavily subsidised for Singaporeans and Permanent Residents. Under HPB's Screen for Life programme offered by most CHAS GP clinics, chronic disease screening (including the doctor consult charges) is available at the following subsidised rates :
Pioneer Generation
If you are a Pioneer Generation cardholder, the screening test and the first post screening consultation (if assessed that a consultation is required) will be $0.
Health Assist (CHAS) Card Holders
If you are a CHAS cardholder (blue or orange card), you will only need to pay $2 for the screening test and the first post screening consultation (if assessed that a consultation is required). Applicable for both males and females aged 40 and above.
Other Eligible Singaporeans
You will only need to pay $5 for the screening test and the first post screening consultation (if assessed that a consultation is required). Applicable for both males and females aged 40 and above.
Permanent Residents
You will only need to pay $10 (excluding GST) for the screening test. The prevailing doctor consultation rates will be charged accordingly by the respective CHAS GP clinics.
*These rates are only applicable at CHAS GP clinics for the screening tests that are covered under the enhanced Screen for Life subsidies. Learn more about the screening tests and subsidies you are eligible for at screenforlife.sg.
Medisave, MediShield Life, ElderShield and Medifund schemes can help Singaporeans offset their medical expenses. Additionally, under the Chronic Disease Management Programme (CDMP), persons with diabetes can also use Medisave to help defray part of outpatient treatment fees and reduce out-of-pocket costs.
[/ACCORDION] [ACCORDION Header="Myths and Facts"]There are many myths about diabetes which people think to be true. This can be harmful as it leads to an incorrect understanding of diabetes. Get the facts below, and learn more about this chronic disease.
MYTH
Diabetes is caused solely by eating too much sweet food.
FACT
Diabetes occurs when the body fails to produce enough insulin – the hormone responsible for reducing blood glucose levels. Although eating sweet food does not directly cause diabetes, a diet high in sugar and fat can lead to obesity, which causes the body to be less sensitive to insulin, thus increasing the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
MYTH
Diabetes can be cured.
FACT
Diabetes is a chronic medical condition that has no cure. However, the condition can be controlled with lifestyle changes and, in some instances, medication.
MYTH
?
FACT
Persons with type 1 diabetes are not able to produce insulin due to an immune disorder affecting the pancreas. That is why they require regular insulin injections to control their blood glucose levels. On the other hand, persons with type 2 diabetes are able to produce insulin, but it may not be enough or may not work properly. Such persons may be prescribed oral medication or insulin injections, or a combination of both by their doctor.
MYTH
People with diabetes will eventually have their feet amputated.
FACT
Amputation refers to the removal of a limb or parts of a limb (e.g. foot) as a result of gangrene or death of body tissues from poor blood flow. It happens in people with long standing diabetes that is poorly controlled. People who take care of themselves by going for regular check-ups, taking medication, and living healthy lifestyles can avoid such complications.
MYTH
People with diabetes should avoid carbohydrates at all costs.
FACT
Carbohydrates are an important part of a healthy, balanced diet. As carbohydrates are found in many foods, including fruits and vegetables, it is not practical to avoid carbohydrates totally. A better option would be to replace the intake of refined, starchy carbohydrates (e.g. white rice) with whole-grains (e.g. brown rice) instead.
MYTH
People with diabetes can safely consume snacks that have “no added sugar”.
FACT
Snacks and candies labelled “no added sugar” or “for diabetics” can be alternative snacks since the former may contain relatively lower sugar content. However, this also means that the sugar in these snacks could have been replaced with artificial sweeteners. Hence, it would be good practice to look at the product contents before purchase, and to consume them in moderation, as snacks labelled “no added sugar” are usually low in nutrient quality.
MYTH
People with diabetes feel unwell.
FACT
Not everyone with diabetes feels unwell. In fact, many people with diabetes do not have any symptoms, particularly during the early stages of the condition. They can have diabetes for months, even years, without knowing it. This is why it is important to go for regular health check-ups, so that you can detect the condition early.
[/ACCORDION] [ACCORDION Header="Signs and Symptoms"]People with type 2 diabetes can feel well and not experience any symptoms at all. However, there may also be symptoms that develop gradually and are sometimes so mild they go unnoticed.
Here are some symptoms that diabetes can cause:
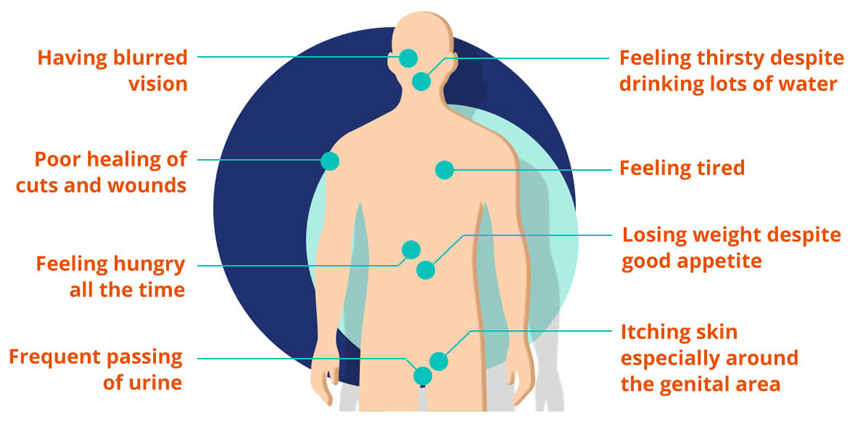 [/ACCORDION]
[ACCORDION Header="Complications"]
[/ACCORDION]
[ACCORDION Header="Complications"]
The high blood glucose (hyperglycemia) levels in uncontrolled diabetes can damage both nerves and blood vessels. As blood vessels supply blood to various organs, this can eventually lead to complications such as:
 Kidney disease
Kidney disease
 Foot disease such as numbness, ulcers, and even gangrene
Foot disease such as numbness, ulcers, and even gangrene
 Eye disease
Eye disease
 Nerve disease which can lead to problems such as erectile dysfunction and diarrhoea
Nerve disease which can lead to problems such as erectile dysfunction and diarrhoea
 Heart disease such as angina and heart attack
Heart disease such as angina and heart attack
 Stroke
Stroke
Being diagnosed with diabetes can be overwhelming. As a caregiver, you want to help your loved ones enjoy the fullest and healthiest life possible.
 The first step to becoming a caregiver to your loved one is to learn as much as you can about diabetes and what lifestyle changes are needed. Going through the change alone can be daunting, so why not make the changes together as a team or family.
The first step to becoming a caregiver to your loved one is to learn as much as you can about diabetes and what lifestyle changes are needed. Going through the change alone can be daunting, so why not make the changes together as a team or family.
 Exercise or shop for diabetes-friendly groceries together, then cook and have meals together. Many lifestyle changes that improve the health of someone with diabetes can also benefit everyone.
Exercise or shop for diabetes-friendly groceries together, then cook and have meals together. Many lifestyle changes that improve the health of someone with diabetes can also benefit everyone.
 Where possible, accompany your loved ones to their medical appointments. Listen, share, and ask questions to help your loved ones get the best care possible from the healthcare team.
Where possible, accompany your loved ones to their medical appointments. Listen, share, and ask questions to help your loved ones get the best care possible from the healthcare team.
 Finally, in the process of being a good caregiver, don’t forget to take care of yourself too.
Finally, in the process of being a good caregiver, don’t forget to take care of yourself too.
 RECOGNISE SIGNS AND SYMPTOMSs
RECOGNISE SIGNS AND SYMPTOMSs
Know what signs and symptoms to look out in a crisis so you can help the person seek immediate attention. Some crises to look out for are:
Diabetes occurs when the body fails to produce enough insulin – the hormone responsible for reducing blood glucose levels. Although eating sweet food does not directly cause diabetes, a diet high in sugar and fat can lead to obesity, which causes the body to be less sensitive to insulin, thus increasing the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
 Hypoglycemia (low blood glucose)
Hypoglycemia (low blood glucose)
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
Shakiness, sweating, weakness, dizziness, irritability, hunger, headache, mood swings, staggering gait
WHAT TO DO:
- Check blood glucose level to confirm; give a glass of fruit juice or 3 to 4 teaspoons sugar in water. Keep some sweets like a bar of chocolate to take for when symptoms occur
- Repeat the above measures in 10 to 15 minutes if blood glucose level is still below 4.0 mmol/l
- Seek immediate medical attention if symptoms persist or if the patient loses consciousness
 Diabetic ketoacidosis
Diabetic ketoacidosis
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
Thirst, fatigue, frequent urination, drowsiness, blurred vision
WHAT TO DO:
- Check blood glucose
- Check urine for ketones if blood glucose is over 240 mg/dl (> 13 mmol/l)
- Continue to drink plenty of water
- Seek medical attention if symptoms persist
 Diabetic ketoacidosis
Diabetic ketoacidosis
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) or diabetic coma is a life-threatening condition that develops when there is too little insulin in the body. This is more common in persons with type 1 diabetes. Without insulin, the body cannot use glucose (sugar) and breaks down fat and protein for energy instead. In the process, it produces a poisonous substance known as ketones. If left untreated, diabetic ketoacidosis can be fatal.
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
Abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, extreme drowsiness, rapid breathing, flushed skin, sweet fruity odour to breath
WHAT TO DO:
- Check that blood glucose levels are above 15mmol/l
- Check urine for ketones. Urine dipstick tests for ketones are available for home use
- Seek immediate medical attention
 CHECK THEIR BLOOD GLUCOSE LEVEL
CHECK THEIR BLOOD GLUCOSE LEVEL
Help the person monitor their blood glucose levels. This requires conducting a blood glucose test at home using a glucometer. Ask the doctor or nurse to help you buy a glucometer.
 Tips on taking a blood sample by finger prick:
Tips on taking a blood sample by finger prick:
- Wash your hands thoroughly before doing the test
- Ensure the person's hand is clean. You can rinse the hands in lukewarm water, then dry them to improve circulation for a better sample
- Do gentle massage of the hands before pricking the finger to improve circulation
- When pricking the finger, use the side of the fingertip rather than the front top so it's less painful
- Apply gentle pressure on the finger pad with the sides pushed out to get a better sample
Your doctor will advise how often the blood test is required.
 MANAGE THEIR DIET
MANAGE THEIR DIET
Get help from a dietician on how to plan meals and adjust the diet. Make positive affirmations each time the person makes a healthy food choice and encourage them to maintain a healthy and well-balanced diet. Here are some tips:
- Use My Healthy Plate as a guide for planning meals
- Choose a variety of foods from the four food groups
- Keep meals regular
- Be mindful of portion sizes when serving food
 ENCOURAGE THEM TO BE PHYSICALLY ACTIVE
ENCOURAGE THEM TO BE PHYSICALLY ACTIVE
Encourage the person to move around more and sit less. Let them know that they do not have to exercise long and hard to reap health benefits. Short bouts of activity break up prolonged seating and improves fat metabolism.
During physical activity, be on the lookout for signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia (low blood glucose). Have some sweets or fruits (e.g. apple) on standby, in case they feel dizzy or weak.
 GIVE THEM THEIR MEDICATION
GIVE THEM THEIR MEDICATION
Most persons with diabetes may also have other medical condition(s) such as high blood pressure, high blood cholesterol level, and may be on medication for such problems. Know what medication(s) the person under your care is taking; understand how it works and its potential side effects. Inform the doctor immediately if the person experiences any reaction to the medication(s).
As a caregiver, ensure that medication is taken or given (in the case of insulin injections) on time and regularly as prescribed by the doctor. Some people with diabetes are afraid of insulin injections, which causes non-compliance in their treatment. Helping them overcome their fear is an important role you can take on.
 CARE FOR THEIR FEET
CARE FOR THEIR FEET
Foot care is very important in persons with diabetes. The person with diabetes may develop foot problems arising from either nerve damage, also called neuropathy, or poor circulation. When sensory nerves of the foot are damaged, the ability to feel sensations, such as pain, is lost and one may be unaware of a wound or breakdown of skin that can lead to infection. Diabetic foot ulcers are serious because they do not heal well and cause gangrene that can lead to amputation.
It is important to keep the blood glucose level under control to minimise the risk of foot problems. As a caregiver, ensure that you assist in the care of the feet every day:
- Wash and inspect feet daily and seek medical care if you spot a problem
- Look for changes in skin colour or feeling
- Gently rub skin lotion over the feet, but not in between the toes
- Trim toenails straight across and file the edges
- Protect feet from extreme temperatures
- Use proper and comfortable foot wear at all times
Additionally, visit the doctor at least once a year for foot examination, and more often if foot problems arise.
[/ACCORDION] [/ACCORDION-WRAPPER][/TAB] [TAB TITLE="Eat Right" COLOR="#86ba2a"]
Nutrition
Whatever your age and condition, eating well has its benefits. A healthy diet and lifestyle can increase your mental sharpness, energy levels, and resistance to illness and disease.
Healthy eating doesn’t have to be about bland and boring food. Eating well should be about a well-rounded diet that follows the principles of a healthy diet. It should be balanced, made up of fresh and tasty food, and above all, enjoyed — whether in the company of family or friends.
A helpful guideline is My Healthy Plate, a friendly visual tool to help you create healthy and balanced meals. On your healthy plate:
Fill half of your plate with fruit and vegetables
Naturally low in fat and rich in vitamins, minerals and fibre, fruit and vegetables add colour, texture, and flavour to your diet. With so many fruit and vegetables in the market, mix and match your choices to get maximum benefit. Remember not to overcook vegetables, and go for whole fruit rather than fruit juices.

Fill a quarter of your plate with whole-grains

Wholegrain foods such as brown rice, wholemeal bread, and rolled oats contain nutrients such as vitamins, minerals, phytochemicals, and inulin. Not only do they protect you from heart diseases and diabetes, they also help manage your weight as they fill you up and you get hungry less easily. On the other hand, refined grains such as white rice and white bread have gone through processing, which removes the valuable nutrients. They also cause a greater increase in your blood glucose levels after a meal.
Choose water
Replacing sweetened drinks with water, and drinking a glass of water before a meal helps you feel fuller and stay slimmer. Drinking water improves blood circulation and prevents muscle cramps so you can engage in regular physical activity and stay healthy. In Singapore’s hot and humid climate, it is important to keep yourself well-hydrated.

Limit alcohol intake

Aim for no more than two drinks per day if you are female, and three drinks per day if you are male. A standard drink is one can (330 ml) of beer, one glass (100 ml) of wine, or one nip (30 ml) of spirits. Beer, wine, and hard liquor contain alcohol –a high source of calories. Regular binge drinking adds inches to your belly and increases your risk of diabetes and heart diseases.
Use healthier oils
Choose unsaturated fats and oils that are healthier, and reduce intake of saturated and trans fats. A diet high in fat can contain calories, thus increasing the risk of obesity and diabetes.

Learning about food groups
If you have diabetes, it is important that you understand how different foods affect your blood glucose levels. Foods are classified into four food groups and they are:
 Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates (starches and sugars)
 Fruits and vegetables
Fruits and vegetables
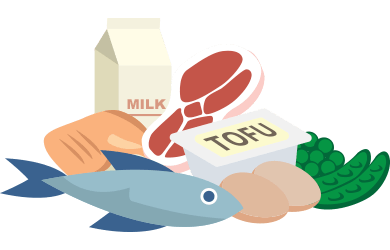 Meat and others
Meat and others (fish, tofu, chicken, beans and nuts, milk and dairy products)
 Fats and oils
Fats and oils
To keep your blood glucose levels within a steady healthy range, choose meals and snacks from each food group every day. The amount of food you consume is just as important as the type of food so learn to control your portion sizes.
[/TAB] [TAB TITLE="Adopt an Active Lifestyle" COLOR="#f48500"]Physical Activity
Want to know what you stand to gain if you stay active? The benefits of being physically active are plenty:
 Helps manage your weight
Helps manage your weight
 Keeps your heart, lungs, and bones healthy
Keeps your heart, lungs, and bones healthy
 Makes you feel good
Makes you feel good
 Keeps diseases away
Keeps diseases away
Before you start planning an exercise routine, take some time to learn more about the variety of physical activities and the benefits they can provide for your body. You will then be able to combine physical activities and get the most out of your exercise routine.
Choose activities that you enjoy and love doing to fit your lifestyle.
Engage in physical activity
To gain health benefits, it is recommended that a healthy person engage in either:
 of moderate-intensity aerobic activity a week, OR
of moderate-intensity aerobic activity a week, OR
 of vigorous-intensity aerobic activity three or more days a week
of vigorous-intensity aerobic activity three or more days a week
The good news is you can:
COMBINE MODERATE AND VIGOROUS-INTENSITY aerobic activity a week for more variety
DO THE AEROBIC ACTIVITY IN SEGMENTS of at least 10 minutes and not have to complete 20 or 30 minutes at one go
Besides aerobic activity, you should also engage in activities that strengthen your muscles two or more days a week. Start with lighter weights or fewer repetitions, and slowly increase the weight over time. A repetition refers to a complete movement of an activity, or the number of times you perform an exercise movement; e.g. 10 sit-ups = 10 repetitions, 15 squats = 15 repetitions. Choose activities that work on different large muscle groups.
| TYPE | BENEFITS | EXAMPLE |
| Aerobic activity makes you breathe harder and your heart beat faster |
Increases heart and lung fitness
Controls weight |
Brisk walking, dancing, cycling, jogging, swimming, and playing badminton |
| Muscle-strengthening activity works on the major muscle groups – the legs, back, chest, belly, shoulders, and arms |
Increases bone strength and muscular fitness
Controls weight Improves balance |
Push-ups, pull-ups, sit-ups, and squats, working with resistance band and weight training |
Exercise at the correct level of intensity
Intensity refers to how hard your body is working during aerobic activity.
| INTENSITY | HOW DO YOU KNOW | EXAMPLES |
| Moderate-intensity aerobic activity | You are still able to talk but not sing or whistle, and are perspiring |
Brisk walking (5 km/hr)
|
Leisure cycling (<16 km/hr)
|
||
Leisure swimming
|
||
Playing badminton (doubles)

|
||
Line dancing
|
||
| Vigorous-intensity aerobic activity | You find yourself breathing hard and fast, and find it hard to hold a conversation with someone |
Jogging or running
|
Swimming continuous laps
|
||
Playing badminton (singles)

|
||
Cycling at a fast pace
|
||
Playing football or basketball

|
FOR YOUR SAFETY: If you have a medical condition, are very overweight or obese and/or have not been exercising for a long time, see your doctor before you start an exercise programme.
[/TAB] [TAB TITLE="Take Control" COLOR="#007dc4"]Self-Care
[ACCORDION-WRAPPER] [ACCORDION Header="Aim For a Healthy Weight"]
Being overweight puts you at risk of numerous health problems including diabetes. Here are some things you should know about why it's important to maintain a healthy weight and how to manage your weight effectively.
How To Achieve A Healthy Weight
In order to achieve a healthy weight, it is important to first understand the dangers of obesity. Obesity is a condition in which excess body fat accumulates and puts you at risk of a variety of health problems. This excess fat may reduce life expectancy and increase the risk of other health problems - so it is vital to maintain a healthy weight.
Know Your BMI
There are many ways to measure body fat. However, the simplest is by calculating your Body Mass Index (BMI). BMI measures the relationship between your weight and height to measure the amount of body fat you have. The higher your BMI, the higher the amount of fat in your body.
Keep an eye on your BMI
Calculate your BMI and keep your BMI in the healthy range (18.5 – 22.9 kg/m2) through an active lifestyle and healthy eating.

Calculate your BMI

Are you in the healthy range? Use this tool to calculate your Body Mass Index (BMI) now to know your health risk.
A BMI value of 23 and above indicates that your weight is outside of the healthy weight range for your height. Find out more on how to achieve and maintain a healthy BMI through a healthy and active lifestyle.
Losing Weight The Right Way
Weight management is all about energy balance. To maintain your weight, you must balance the amount of energy you get from food and drinks with the amount of energy your body uses for daily physical activity. Consuming more energy than you need will lead to weight gain, while burning more energy than you consume will lead to weight loss.
 [/ACCORDION]
[ACCORDION Header="Quit Smoking"]
[/ACCORDION]
[ACCORDION Header="Quit Smoking"]
Smokers are more likely to develop type 2 diabetes. People with diabetes who smoke experience more problems with their diabetes control than those who don’t. They are also more likely to end up with diabetes complications.
What’s more, smoking damages the blood vessels and reduces blood flow to many organs. So if you have diabetes and smoke, you are at a higher risk of serious complications, such as heart disease, amputation, and stroke.
If you do not smoke, continue to stay smoke-free and enjoy the health benefits it brings.
If you smoke, make the decision to quit smoking today. The good news is that there is a range of support strategies to help you quit smoking. It is a matter of finding the right one for you.
 Choose a quit method that suits you best
Choose a quit method that suits you best
You can choose to:
 Quit "cold turkey"
Quit "cold turkey"
 Gradually cut down on the number of cigarettes
Gradually cut down on the number of cigarettes
 Seek professional help
Seek professional help
 Use nicotine replacement therapy
Use nicotine replacement therapy
 Take medication
Take medication
 Attend a self-help group
Attend a self-help group
 Whichever method you choose, remember there’s no magic formula to quitting. For professional help, call QuitLine at 1800 438 2000.
Whichever method you choose, remember there’s no magic formula to quitting. For professional help, call QuitLine at 1800 438 2000.
You will be encouraged to know that many people make several attempts to quit smoking before they manage to successfully break free from the habit. So if you fail to quit on the first attempt or experience any relapses long the way, do not give up and try again.
[/ACCORDION] [ACCORDION Header="Mental Well-being"]Stress can raise blood pressure and blood glucose levels. It can also affect how well you manage medical conditions. Here are some tips to improve your mental well-being:
Have enough sleep
Besides causing you to lose focus and increasing the risk of accidents, sleep deprivation has been linked to several health conditions including heart disease, high blood pressure, stroke, and diabetes. Lack of sleep may be associated with an increase in hunger and appetite, as well as obesity. If you experience problems sleeping and it is affecting your personal and work life, see a doctor to rule out underlying medical conditions.
Think positive
The way you think affects how you feel about people, things and situations as well as how you respond to them. The ability to think positive and embrace optimism is linked to many health benefits. It doesn’t suggest burying your head in the sand and ignoring problems you have. Positive thinking simply means that you approach the negative things in life in a more positive and productive manner. Not only does it help you cope better with stressful situations, it also reduces the harmful effects stress has on your body. It is also believed that positive people tend to take better care of themselves. They eat more healthily, get more physical activity, do not smoke, and do not drink alcohol in excess.
Be mindful
Being mindful is to be aware of your thoughts, feelings and environment, moment by moment. Instead of harping on the past or worrying about the future, mindfulness brings your attention to the present – helping to clear your mind of mental clutter and focus on positive feelings and thoughts. Take time to breathe in and breathe out, to savour the food you eat, or simply to enjoy the sunset – these are all simple and effective ways of being mindful.
Managing stress

Stress, especially chronic stress, can have a negative effect on blood glucose levels. People under stress tend not to take care of themselves. They may drink and eat excessively, exercise less or not have enough sleep. They may forget or not have the time to check their blood glucose or prepare healthy meals.
[/ACCORDION] [/ACCORDION-WRAPPER] [/TAB] [/TAB-WRAPPER]


