As a person with diabetes, you cannot be in the care of a doctor or a nurse all the time. Therefore, it is very important for you to learn how to manage your diabetes well. The main goal is to keep your blood glucose at an optimal level and not too high or too low
How Do I Manage Diabetes?
Diabetes is normally treated first with weight loss, diet and exercise. When these fail to work, oral medications will be given. If these are not enough to control diabetes or if your diabetes is long-standing, your doctor will consider prescribing insulin for you.
Maintaining a Healthy Weight
If you are overweight, aim to lose some weight. Studies have shown that losing five percent of your weight can very much improve your diabetes control.
A Body Mass Index (BMI) between 18.5 and 23 is considered healthy. You can calculate your BMI using the following formula:
BMI = Weight (kg) ÷ [Height (m) x Height (m)]
For example, if you weigh 60kg and are 1.70m tall, your BMI will be 60 ÷ (1.70 x 1.70) = 20.8
Eating a Healthy Diet
There is no special diet for people with diabetes. You can enjoy the same healthy meals as everyone else.
However, you have to be very careful about the amount of carbohydrates you eat everyday, as carbohydrates can cause blood glucose levels to rise the most. The amount of fat and protein taken has to be closely monitored too, since they indirectly affect your blood sugar levels.
Use the healthy diet pyramid below as a guide to make sure your meals are balanced and come from different food groups.

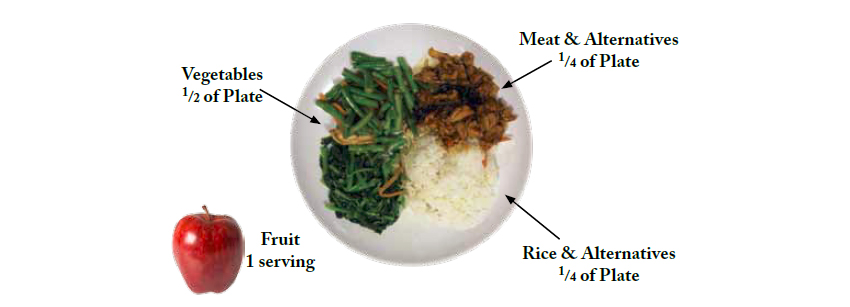
This is how your plate should look like if you were to follow the healthy diet pyramid way of eating, using a 12-inch plate.
Tips from other patients about healthy eating
I drink diet soft drinks instead of regular ones.
I bring a little bag of walnuts around with me to snack on when I’m hungry.
I used to skip breakfast, but now I have breakfast every morning to give me more energy.
Tips for Healthy Eating in Diabetes
Eat small and regular meals.
Eat breakfast, lunch and dinner at regular times, and have a small snack in between these meals. You can keep your blood glucose levels within the target range by spreading the carbohydrates that you eat evenly throughout the day.
Reduce amount of fats, salt and sugary foods.
Eat more foods that are high in fibre, including wholegrain products.
Match your meal times to the timing and frequency of your medications.
If you choose your food wisely, you may be able to control your diabetes with fewer medications. Eating regularly and healthily is the key to good diabetes control. Your dietitian will be able to assist you further in your meal plan.
Exercise Regularly
How Do I Keep Active?
If you have decided to start an exercise programme, congratulations! Getting fit is part of staying healthy and fighting against diabetes. Still, it does not mean you have to exercise for hours each day to achieve your goal. You can manage your diabetes better just by being active. It can be just a few minutes of walking a day, or even cycling for five minutes everyday.
Together with your meal plan and medications (where needed), regular exercise improves and controls diabetes by lowering your blood glucose level. In addition, exercising helps in controlling your weight, improving your blood and has many other benefits.
How Do I Get Started?
Talk to your doctor or physiotherapist: Find out what exercises are suitable for your current condition. A physiotherapist can assess your fitness level and help you develop an exercise plan.
Set realistic goals: Take small steps at first. Pick an activity you are sure you will be able to do. You can increase the frequency and intensity later when you feel comfortable doing more.
Develop your exercise plan:
Use the F.I.T.T. formula
F = Frequency: how often will you exercise?
I = Intensity: how hard will you exercise?
T = Time: how long will you exercise?
T = Type: which types of exercise will you choose?Start acting on your plan!
How Do I Get Started? How Often Should I Exercise?
Exercise regularly, no matter what exercise you choose to do. This is especially so if you are taking insulin.
Aim to do 150 minutes of moderate intensity exercises per week. Each exercise should last at least 10 minutes. If you have not been active, start slowly.
How Hard Should I Exercise?
Aim to work at a moderate level of intensity. Working out at this level makes you feel warm and breathe more heavily, yet still able to talk comfortably. You can start increasing the intensity of your exercise once you feel comfortable doing more.
How Long Should I Exercise?
If you haven’t been exercising, you can start with 10 minutes a day. It can be as easy as walking five minutes from your block, then turning around and walking back. After a week, add another 10 minutes of exercise. Before long, you will be able to exercise up to 30 minutes. You may also exercise 10 minutes three times a day to make up the 30 minutes.
What Type of Exercises Can I Do?
The best form of exercise is something you enjoy doing, and preferably using large muscle groups in your body constantly, over a period of time.
The three main types of exercises are:
Aerobic exercises: also called cardiovascular or endurance exercises. These include walking, jogging, swimming, dancing and ball games.
Flexibility exercises: including stretching, which help to loosen muscles and joints. Do these exercises slowly, holding each stretch for a few seconds.
Strengthening exercises: these make your muscles stronger by working them harder. Strengthening exercises are usually done against resistance, such as lifting weights. Do not hold your breath while doing strengthening exercises.
Tips from other patients about exercising
I take part in line dancing at the community centre.
I park further away in the car park to help me walk a bit more.
I alight from the bus one stop earlier to walk a longer distance home.
I climb the staircase instead of the lift or escalator.
What Exercises Can I Do If I Have Trouble Walking?
You can try
water aerobics
cycling
upper body stretching
lifting weight while sitting
Some tips from other patients with trouble walking:
I can still sit in my chair and lift weights. I just use mineral water bottles.
I do what I can. I wheel myself around instead of having someone always pushing me in my wheelchair.
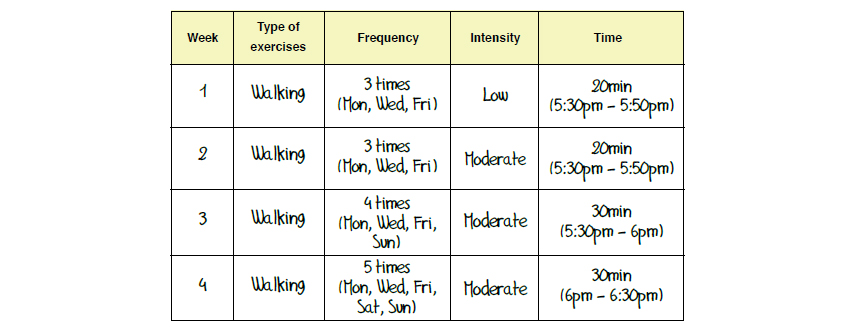
Example of a 1-month exercise plan:
Safety Precautions: Before You Start
Check your blood glucose level just before you exercise. If your blood glucose level is:
Below 6mmol/L (100mg/dl) – Eat a small low-fat snack before exercise.
Above 22mmol/L (370mg/dl) – Do not exercise now. Drink more water.
If you are above 40 years old, or have underlying heart disease, consult your diabetes care team before considering vigorous exercise.
If your feet are numb, you can’t see clearly or have bleeding in the eye, consult your diabetes care team before exercising.
If you are exercising right before your next meal, take a small snack half to one hour before you exercise.
If you are on insulin, you will need even more care during and after exercise to prevent a low blood glucose level. Your diabetes care team will be able to advise you on this.
Other precautions to take:
Oral Medication
There are many different types of tablets available to treat diabetes. These tablets, in addition to the meal plan and exercise plan, help you manage your blood glucose level. They work by helping:
your pancreas to release more insulin, e.g. Glipizide
your body to use insulin more efficiently, e.g. Metformin
to stop the quick rise of blood glucose after a meal, e.g. Acarbose
What Precautions Should I Follow?
Before taking your medicine, inform your doctor if you:
have any allergy
are on any medication
have heart, kidney or liver problems
are going for any surgery
are pregnant or planning to get pregnant
are breastfeeding
What Must I Do While Taking the Medication?
Take your medicine regularly and exactly as prescribed by your doctor.
Do not stop taking your medicine without consulting your doctor.
If you miss a dose, take the missed dose as soon as you remember. However, if it is almost time for the next dose, take only the next dose. Do not double the dose. It is good to check with your doctor at your next visit for specific advice.
If you visit another doctor, be sure to tell him you are taking this medicine.
How Do I Store My Medicine?
Store your medicine in a cool,dry place. Keep each medicine separately in its original labelled container. Never mix your medication into one container.
What Are The Possible Side Effects of the Medicine?
Low blood glucose (hypoglycaemia)
This may happen if you have taken your medicine but do not eat your meals on time, or have poor appetitie because you feel sick. Signs of low blood glucose include sweating, trembling, fast heartbeat, feeling very hungry, double vision, weakness, and dizziness.
When you experience these symptoms, you should eat some sugar cubes or drink honey immediately. Call your doctor if you still feel faint.
Stomach discomfort / diarrhoea
Consult your doctor if these symptoms are severe or do not go away. If you have a skin rash after taking the medicine, inform your doctor immediately as this may be an allergic reaction.
Tips from other patients about taking medicine
I use a pillbox to remind me if I have taken my pills everyday.
My doctor taught me to take my pills at the same time every day. It keeps my blood glucose level from going too high or too low.
My son and I made a medication list of all the medicines I take. This makes it easy.
I bring my medication list to my doctor. This helps her understand me better.
There may be times when the usual oral medications are not effective, especially in long-standing diabetes. Your doctor will prescribe you insulin to control your blood glucose level. Many patients do much better on daily injections of insulin. This does not mean that their diabetes is worse or that they have “failed” in their diet and exercise regimen.
Contributed By: Health Promotion Board (HPB)
Diabetes Management: Weight, Diet, Exercise and Medicine by Health Promotion Board, 5 May 2020, www.healthhub.sg.