Early detection prevents complication such as heart failure, stroke, kidney disease and artery disease. This article details an individual's risk to the disease as well as recommendations for prevention.

Heart disease is a leading cause of death worldwide, and affects not only the heart but other major parts of the body. Early detection prevents complication such as heart failure, stroke, kidney disease and artery disease. This article details an individual s risk to the disease as well as recommendations for prevention.
Heart (Cardiovascular) Screening
Heart disease is a broad term that describes a range of diseases of the heart and blood vessels. Heart disease is often used interchangeably with cardiovascular disease.
The disease is a leading cause of deaths worldwide and refers to disorders of the blood vessels supplying the heart and other major parts of the body. Early detection reduces suffering and prevents complications such as heart failure, stroke and kidney disease through early treatment.
Why is cardiovascular screening important?
Cardiovascular disease begins with damage to the body from lifestyle factors of smoking, physical inactivity and unhealthy diet. This progresses to the development of high-risk diseases such as obesity, high blood pressure and diabetes. Screening identifies those at risk of future cardiovascular events of the heart and other major body organs. It also identifies those with modifiable risk factors, which are reversible and reduce one s risk of developing cardiovascular disease.
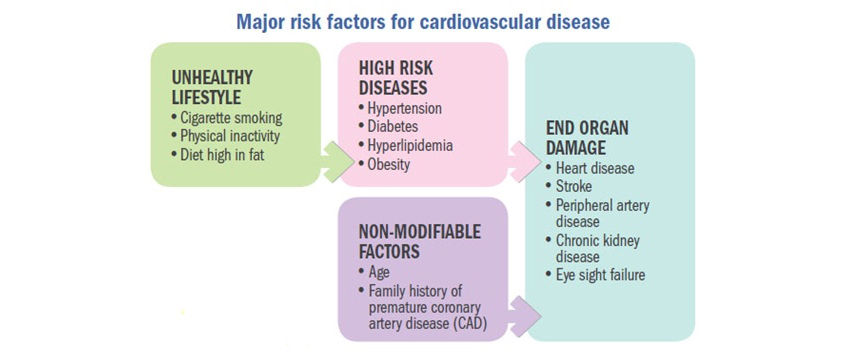
Who should go for screening of cardiovascular risk factors?
Every adult aged 18 years and above should go for screening of cardiovascular risk factors. Patients with diabetes, high blood pressure and long-standing kidney disease have a higher risk for cardiovascular disease and should be screened regularly based on their doctor's advice.
Cardiovascular risk assessment
What is global cardiovascular risk assessment?
Global cardiovascular risk assessment involves assessing a patient s total cardiovascular risk rather than just assessing risk factors (high cholesterol, blood pressure, diabetes or obesity) in isolation. The best known global cardiovascular risk assessment tool is the Framingham Risk Score (FRS). Based on the FRS adapted for local use, the risk for an asymptomatic individual is classified as:
- Low-risk corresponding to <10% risk of vascular events* over a ten-year period
- Intermediate-risk corresponding to 10-20% risk of vascular events over a ten-year period
- High-risk corresponding to >20% risk of vascular events over a ten-year period
*These vascular events include heart attack and coronary death.
It should be done every five years starting from the age of 18 years. For individuals at risk but who have no symptoms, the assessment is followed by advice on making certain lifestyle changes such as cutting back on cigarettes, eating healthy foods and exercising regularly and, where appropriate, medicines are given to treat high blood pressure, high lipids and diabetes. Individuals at low risk should continue to lead a healthy lifestyle. More frequent assessment is recommended for those who are diabetic, chronic smokers or obese.
How to calculate the ten-year coronary artery disease risk?
It is calculated based on:
- Age
- Sex
- Ethnicity
- Smoking status
- Total and High Density Lipoprotein (HDL) or good cholesterol level
- Systolic blood pressure
Additional screening tests
What additional screening tests may be needed following global cardiovascular risk screening?
These additional tests may be needed for cardiovascular evaluation of individuals at moderate and high risk without any symptoms.
| Additional Screening Tests | Remarks |
|---|---|
| Resting Electrocardiogram (ECG) | Indicated only in selected individuals e.g., cardiovascular screening in asymptomatic people with high blood pressure |
| Exercise Treadmill Test | Recommended in individuals without symptoms:
|
| Coronary artery calcium score | Recommended in patients who have atypical chest pain to rule out ischaemic heart disease (These patients are otherwise considered to be at low-risk of coronary disease) |
| Cardiac stress imaging (stress echocardiography) | Reserved for individuals with an abnormal exercise ECG |
| CT coronary angiography | Uncertain value as a screening test even in high-risk individuals. The risks of the test and the possibility that it may lead to further unnecessary tests need to be considered |
| Carotid intima-media thickness | Not recommended for routine cardiovascular screening |
When should screening for body mass index (BMI), waist circumference, high blood pressure and high cholesterol be done?
| Recommended for | To screen for | Screening test | Screening frequency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Individuals aged 18 years and above | Obesity | Body Mass Index (BMI) | Once a year |
| Obesity | Waist Circumference | ||
| Individuals aged 18 years and above | High blood pressure | Blood pressure measurement | Once every two years or more frequently as advised by your health care provider |
| Individuals aged 40 years and above (Younger age group e.g. 30 years if other risk factors for diabetes or high lipids are present) |
Diabetes mellitus | Fasting venous blood glucose | Once every three years or more frequently as advised by your health care provider |
Pre-exercise screening
What is pre-exercise screening?
It helps identify those at risk for a cardiovascular event during exercise. The questionnaire below is recommended for safety reasons before participating in any physical activity.
Table 5: Physical Activity Readiness Questionnaire (PAR-Q)
Before you exercise, please read each question carefully and answer Yes or No to your best knowledge.
| 1) Has anyone in your immediate family (mother, father, sister or brother) had a heart attack or died suddenly of a heart related disorder before age 55 (men) or 65 (women)? | Yes | No |
2) Has your doctor informed you that you have any of these conditions? (check all that apply)
|
Yes | No |
| 3) Do you feel pain or discomfort in your chest when you engage in physical activity? | Yes | No |
| 4) In the past one year, have you had chest pain when you were NOT engaging in physical activity? | Yes | No |
| 5) Do you ever experience dizziness or even lose consciousness? | Yes | No |
| 6) Do you have any bone, joint or muscle problem (e.g. back, knee, hip, shoulder or ankle) that could be made worse by participating in exercise? | Yes | No |
| 7) Are you taking medication for high blood pressure or a heart condition? | Yes | No |
| 8) Are you currently pregnant? (Female participants if you are currently pregnant please speak with your doctor about an appropriate exercise programme) | Yes | No |
| 9) Do you know of any reason why participating in any other physical activity might be harmful to your health? | Yes | No |
| If you answered YES to one or more questions: Talk with your doctor in person before you proceed with any exercise programme. |
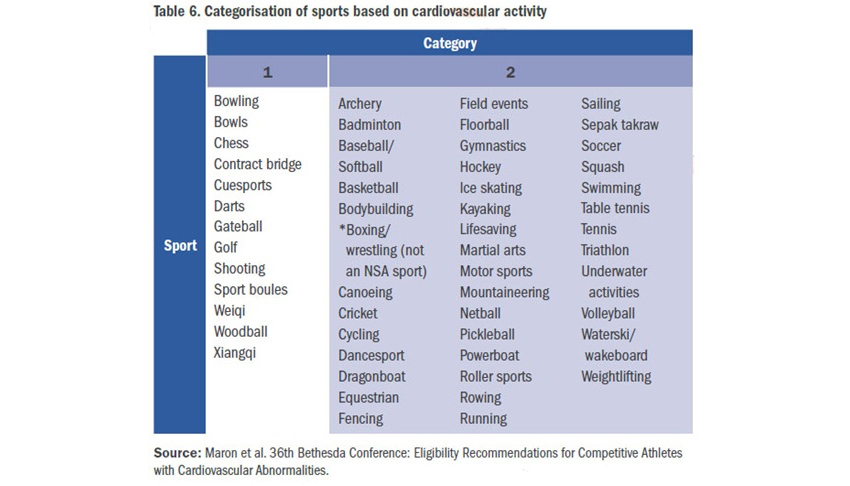
Physical activities are categorised into Category 1 and Category 2 (Table 6) based on the requirement of cardiovascular fitness.
For Category 2 activities, greater cardiovascular fitness is needed along with a physical fitness clearance by a doctor
For Category 1 activities, physical fitness is still an important consideration
For example, in a physically fit 55-year-old adult, Category 1 activities will pose no problem whereas an unfit person with congestive heart failure may not be able to tolerate such activities.
Follow-up on the results of screening for cardiovascular disease and risk factors
Talk about the results of your screening with your doctor and know what you can do to live a healthy lifestyle (Table 7) as well as ways to prevent and treat your medical conditions (Table 8).
Table 7. Live a healthy lifestyle
| What you can do | Recommendations |
|---|---|
| Healthy eating |
|
| Maintain a healthy weight |
|
| Engage in regular physical activity |
|
| Cut back on cigarettes | See your doctor if you need help to quit smoking or to discuss more about it |
| Limit alcohol use |
|
Table 8. Prevent and treat your medical conditions
| What you can do | Recommendations |
|---|---|
| Keep your cholesterol levels in check | Desirable levels are:
|
| Keep your blood pressure levels in check | Normal blood pressure levels are:
|
| Keep your blood sugar levels in check | Optimal (target goal for majority of patients) are:
|
| Take your medications regularly |
|
| Go for regular monitoring if you have chronic medical conditions |
|